What is the Tax-to-GDP Ratio?
Tax-to-GDP ratio is a factor that signifies the size of the tax kitty of a nation in relevance to its Gross Domestic Production (GDP). Basically, it signifies the size of tax revenue that the government collected in a specific year.
Expressed in the form of a percentage, if the tax-to-GDP ratio is higher, it shows the better and adequate financial position of a country and vice versa. It denotes that a country is capable of financing its expenses. Also, a high tax-to-GDP ratio also denotes that the government is competent enough to cast fiscal net wide; thus, ultimately decreasing the dependency of a country on borrowings.
Why is Tax-to-GDP Ratio Important?
If this specific ratio is on the higher end, it means that the tax resilience of an economy is stronger as the tax revenue share increases in synchronization with the increase in the GDP of the country. As far as India is concerned, despite experiencing higher growth rates, the country has been struggling to broaden its tax base.
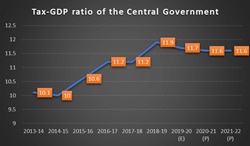
On the other hand, low tax-to-GDP ratio compels the government to spend more on infrastructure. Not just that, it also pressurizes the government to accomplish its fiscal deficit objectives. The average OECD ratio in the world is 34%. And, despite improving its economy, India has plunged to the lowest of 9.88% for the FY20, which is the lowest in the last 10-years. This ratio was driven by a decrease in collections from corporation tax and customs duties.
This decline still existed, given the fact that the nation only had a week or so under complete lockdown in 2020. For FY19, this ratio stood at 10.97%, and for FY18, it was at 11.22%. The tax-to-GDP ratio of India is only predicted to decrease more with revenues reducing on account of a fall in the economy.
In comparison to India, developed countries have more contribution to taxes; thus, a higher tax-to-GDP ratio. In FY20, the gross tax revenue of the centre fell down to 3.39% with a massive Rs. 1.5 trillion shortfalls in accumulation, which is clearly against the revised budget target. Furthermore, to accomplish the budget target, India will need growth of almost 20.5% in FY21.
Talk to our investment specialist
How can Tax-to-GDP Ratio be Improved?
- One of the most vital measures to improve this ratio is by making sure that the citizens are paying taxes on time
- By introducing the Direct Tax Code, better compliances can be implemented in this regard
- GST rationalisation and going toward a two-rate structure may also help in terms of increased compliance; it may also help to end tax evasions
- More and cautious focus should be kept on higher economic growth
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.












