Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate
Central banks rely on various monetary policy tools to manage inflation and promote economic growth, including repo rate and reverse repo rate. In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) sets these rates to help regulate the economy and maintain stability in financial markets. As of April 2023, the current repo rate is 4.00%, and the current reverse repo rate in India is 3.35%, both having been kept unchanged in the latest RBI monetary policy announcement. Businesses, investors, and the general public need to understand the difference between these rates and their economic impact. In this article, you'll delve deeper into repo rate vs reverse repo rate and explore its significance in the Indian economy.

What is Repo Rate?
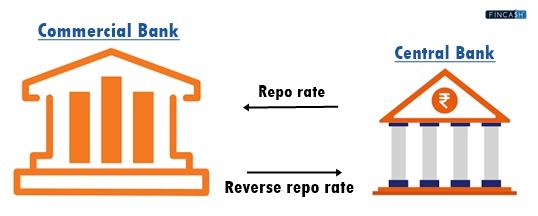
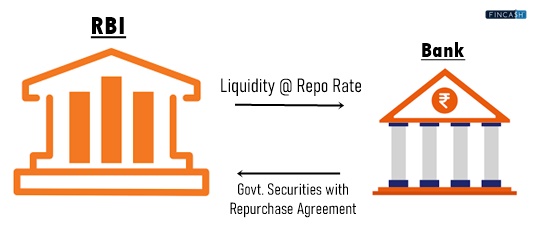
The repo rate is the short-term lending rate at which commercial banks can borrow money from the central bank. This interest rate is a key tool the central bank uses to manage liquidity and inflation in the financial system.
How does Repo Rate work?
Repo rate works by the central bank offering short-term loans to commercial banks at a fixed interest rate. When commercial banks need extra funds, they have a valuable option: they can sell securities to the central bank and agree to repurchase them later at a slightly higher price. This way, the banks can access the liquidity required to keep their operations running smoothly. This process is known as a repurchase agreement or repo.
The RBI's Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decides on the repo rate during its bi-monthly meetings based on economic factors such as inflation and growth and external factors like global economic conditions. A repo rate is a powerful tool for the central bank to control the money supply in the economy and to achieve its monetary policy objectives. Repo rate affects the economy by influencing the cost of borrowing for commercial banks and, in turn, affecting the lending rates for businesses and consumers. A higher repo rate can lead to higher borrowing costs, reducing the demand for credit and slowing economic growth.
Talk to our investment specialist
What is Reverse Repo Rate?
When commercial banks invest in government securities, they have the opportunity to earn interest by lending money to the central bank. This interest rate is known as the reverse repo rate. It is the opposite of the repo rate, as the central bank borrows money from commercial banks instead of lending. The reverse repo rate is also set by the RBI and is used to regulate liquidity in the banking system.
How does Reverse Repo Rate work?
The reverse repo rate works by the central bank borrowing money from commercial banks by offering government securities as Collateral. Commercial banks invest surplus funds in these securities and earn interest on their investment, which is the reverse repo rate. The higher the reverse repo rate, the more attractive it is for banks to lend to the central bank and park their excess funds with the central bank instead of lending them to customers. Reverse repo rate affects the economy by influencing the interest rates banks offer customers. A higher reverse repo rate can incentivise banks to park their funds with the central bank instead of lending to customers, reducing credit availability and slowing economic growth.
Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate
The key difference between the repo rate and reverse repo rate is:
Direction of the Transaction: In the repo rate, the central bank lends money to commercial banks, while in the reverse repo rate, the central bank borrows money from commercial banks.
Purpose of Transaction: The purpose of the repo rate is to inject liquidity into the economy and regulate inflation. The purpose of the reverse repo rate is to absorb excess liquidity in the banking system and control inflation.
Interest Rates: The interest rate on the repo rate is higher than the reverse repo rate as it involves lending money, whereas the reverse repo interest rate is lower as it involves borrowing money.
Participants: In the repo rate, only banks can borrow from the central bank, while in the reverse repo rate, both banks and non-bank financial institutions can lend to the central bank.
Risk: The risk associated with the repo rate is higher for the central bank as it involves lending money to banks. In comparison, the risk associated with the reverse repo rate is lower as it involves borrowing money from banks, which is considered safer.
Differences that Impact the Economy?
These differences between the repo rate and reverse repo rate impact the economy in the following ways:
Liquidity and Interest Rates
The repo rate influences liquidity in the economy by regulating the cost of borrowing for commercial banks, which affects the lending rates for businesses and consumers. A high repo rate reduces liquidity, while a low repo rate increases liquidity. In contrast, the reverse repo rate impacts the interest rates banks offer customers. A high reverse repo rate encourages banks to park their funds with the central bank, reducing credit availability and raising interest rates for borrowers.
Inflation
Repo rate and reverse repo rate impact inflation in the economy. A high repo rate reduces borrowing and spending, lowering demand and inflation. On the other hand, a high reverse repo rate reduces credit availability, leading to lower spending and lower inflation.
Monetary Policy
The central bank uses the repo rate and reverse repo rate to implement its monetary policy objectives. The central bank can influence the money supply, inflation, and economic growth by adjusting these rates.
Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate: A Comparative Analysis of their Relationship
The relationship between the repo rate and reverse repo rate is that they are two sides of the same coin and impact each other. When the central bank increases the repo rate, it becomes more expensive for commercial banks to borrow money, which reduces their ability to lend to businesses and consumers. This, in turn, reduces the liquidity in the economy and can slow down economic growth.
In contrast, when the central bank increases the reverse repo rate, it becomes more attractive for commercial banks to lend money to the central bank instead of lending to businesses and consumers. This reduces credit availability in the economy and can slow economic growth.
Therefore, the central bank must maintain a balance between these two rates to ensure that the economy remains stable and grows at a sustainable pace. A change in one rate can impact the other rate and the overall liquidity in the economy, and hence the central bank must carefully consider its monetary policy objectives before adjusting these rates.
Repo Rate Vs Bank Rate
Repo rate and bank rate are two different rates used by central banks to manage the monetary policy of a country.
The repo rate is the rate at which commercial banks borrow money from the central bank, usually on a short-term basis. It is used to regulate the liquidity in the economy, control inflation, and stimulate economic growth. An increase in the repo rate makes borrowing more expensive, reducing liquidity and slowing down economic growth, while a decrease in the repo rate makes borrowing cheaper, increasing liquidity and stimulating economic growth.
Bank Rate, on the other hand, is the rate at which the central bank lends money to commercial banks, usually on a long-term basis. It is used to regulate the overall money supply in the economy, control inflation, and stabilise the financial system. An increase in bank rate makes borrowing more expensive for banks, reducing the overall money supply in the economy and controlling inflation, while a decrease in bank rate makes borrowing cheaper for banks, increasing the overall money supply and stimulating economic growth.
Implications for Businesses and Investors
The implications of repo rate and reverse repo rate for businesses and investors are as follows:
Cost of Borrowing
The repo rate influences the cost of borrowing for businesses, which affects their profitability and growth prospects. A high repo rate increases the cost of borrowing, making it more expensive for businesses to raise funds for investment and expansion. In contrast, a low repo rate makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money and invest in their growth.
Availability of Credit
Reverse repo rate influences the availability of credit for businesses and investors. A high reverse repo rate reduces the availability of credit, making it harder for businesses to raise funds and invest in their growth. In contrast, a low reverse repo rate increases the availability of credit, making it easier for businesses to raise funds and invest in their growth.
Investment Decisions
Repo rate and reverse repo rate also impact investment decisions by investors. A high repo rate may make fixed-income investments such as Bonds more attractive as they offer higher returns, while a low repo rate may make equity investments more attractive as businesses can borrow money cheaply to invest in their growth. Similarly, a high reverse repo rate may make fixed-income investments more attractive as banks can park their funds safely with the central bank, while a low reverse repo rate may make equity investments more attractive as banks lend more to businesses and investors.
Economic Growth
Repo rate and reverse repo rate have a significant impact on the overall economic growth of the country. A high repo rate can slow down economic growth by reducing liquidity and making borrowing expensive, while a high reverse repo rate can also slow down economic growth by reducing the availability of credit. In contrast, a low repo rate and reverse repo rate can stimulate economic growth by increasing liquidity and the availability of credit.
The Bottom Line
Repo rate and reverse repo rate are crucial tools used by central banks to regulate liquidity, interest rates, inflation, and economic growth. These rates impact businesses, investors, and consumers in various ways, influencing borrowing costs, availability of credit, and investment decisions. A change in one rate can impact the other rate and the overall liquidity in the economy. Therefore, policymakers and analysts must carefully consider these rates when formulating economic policies and making investment decisions. A balanced approach to maintaining these rates is crucial for ensuring stable economic growth and a healthy investment climate.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.