What is Enterprise Risk Management Framework?
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) considers risk management from the perspective of the entire company or organization. It's a top-down risk management methodology that identifies, assess, and prepares for potential losses, dangers, hazards, and other forms of harm that could disrupt an organization's operations, objectives and result in losses.
ERM is a holistic approach that necessitates management-level decision-making that may or may not be appropriate for a specific business unit or sector. As a result, the firm's monitoring is prioritized instead of each business unit being accountable for its risk management.
For example, if a risk manager at an investment Bank finds that two trading desks in separate parts of the firm have equal exposures to the same risk, the less significant of the two may be forced to minimize that risk. This choice is taken with the company as a whole in mind (not with the specific trading desk).
Briefly Understanding ERM
ERM not only requires companies to identify all of the risks they face and decide which risks to actively manage (as other forms of risk management do), but it also allows top executives to make executive risk management decisions that may or may not be in the best interests of a specific segment—but that is best for the company as a whole.
It is because risks might be categorized in specific business units that do not or cannot perceive the big picture. It also frequently entails distributing the risk action plan to all stakeholders as part of an Annual Report. ERM is now used in industries as diverse as construction, aviation, international development, public health, finance, energy, and insurance.
Businesses have used risk management for many years. Traditionally, risk management has relied on each business unit assessing and managing its own risk before reporting back to the CEO. Companies have recently begun to see the need for a more comprehensive strategy.
While ERM best practices and standards are continuously growing, COSO, an industry body that monitors and updates such guidelines for businesses and ERM practitioners, has institutionalized them.
Talk to our investment specialist
Risk Types
- Hazard risks are those that provide a significant risk to one's life, health, or property.
- Risks that are directly tied to money are referred to as financial risks. They include financial effects such as cost increases or income decreases.
- Strategic risks are those that are influenced or created as a result of strategic business decisions.
- Operational risks are those that have a significant impact on a company.
Enterprise Risk Management Examples
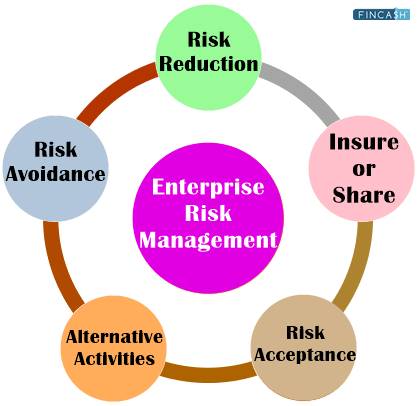
To deal with their identified risks, management chooses one of the five risk response strategies listed below:
- Risk avoidance: It is the process of removing dangers or activities that can harm an organization's assets. For example, a proposed production or product line may be cancelled or halted.
- Risk reduction: It is the process of reducing or limiting the severity of losses. Management, for example, should schedule frequent visits to its big suppliers to see possible problems early.
- Alternative activities: It includes thinking about various methods to lessen hazards.
- Insure or Share: Transferring risks to third parties, such as insurance firms, is known as sharing or insuring. For example, purchasing an insurance policy to cover any unforeseen company losses.
- Risk acceptance: It is defined as the acceptance of identified hazards and the readiness to accept the consequences of those risks. Risk acceptance is typically defined as any loss resulting from a risk that was not covered or prevented.
Components of Enterprise Risk Management
To secure financial stability for firms, ERM follows a highly different and ongoing procedure in which it actively detects and reassesses the numerous strategic and primary risks. There are five distinct elements to the procedure:
- Strategy/Objective setting: Understanding the business's strategies and associated risks (Strategy/Objective setting).
- Risk identification: Provide a clear profile of main risks that could negatively influence the company's overall financials.
- Risk assessment: Once hazards have been identified, they are thoroughly examined to establish their likelihood and potential.
- Risk response: Think about several risk response tactics and choose the best actionable approaches to match detected risks to management's risk tolerances.
- Communication and monitoring: Relevant data and information must be regularly monitored and communicated across all levels of the organization.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.